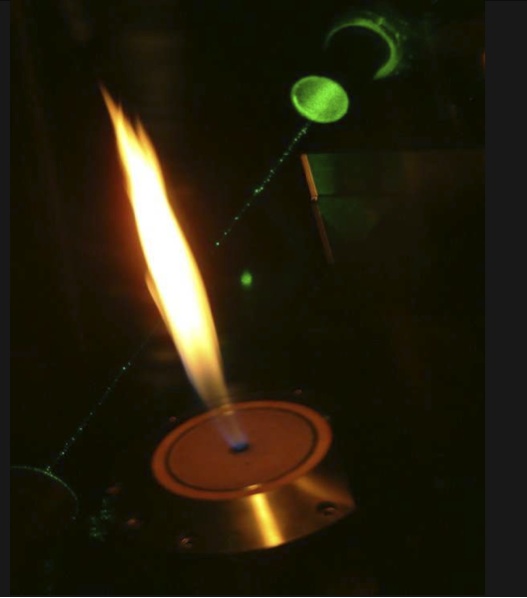
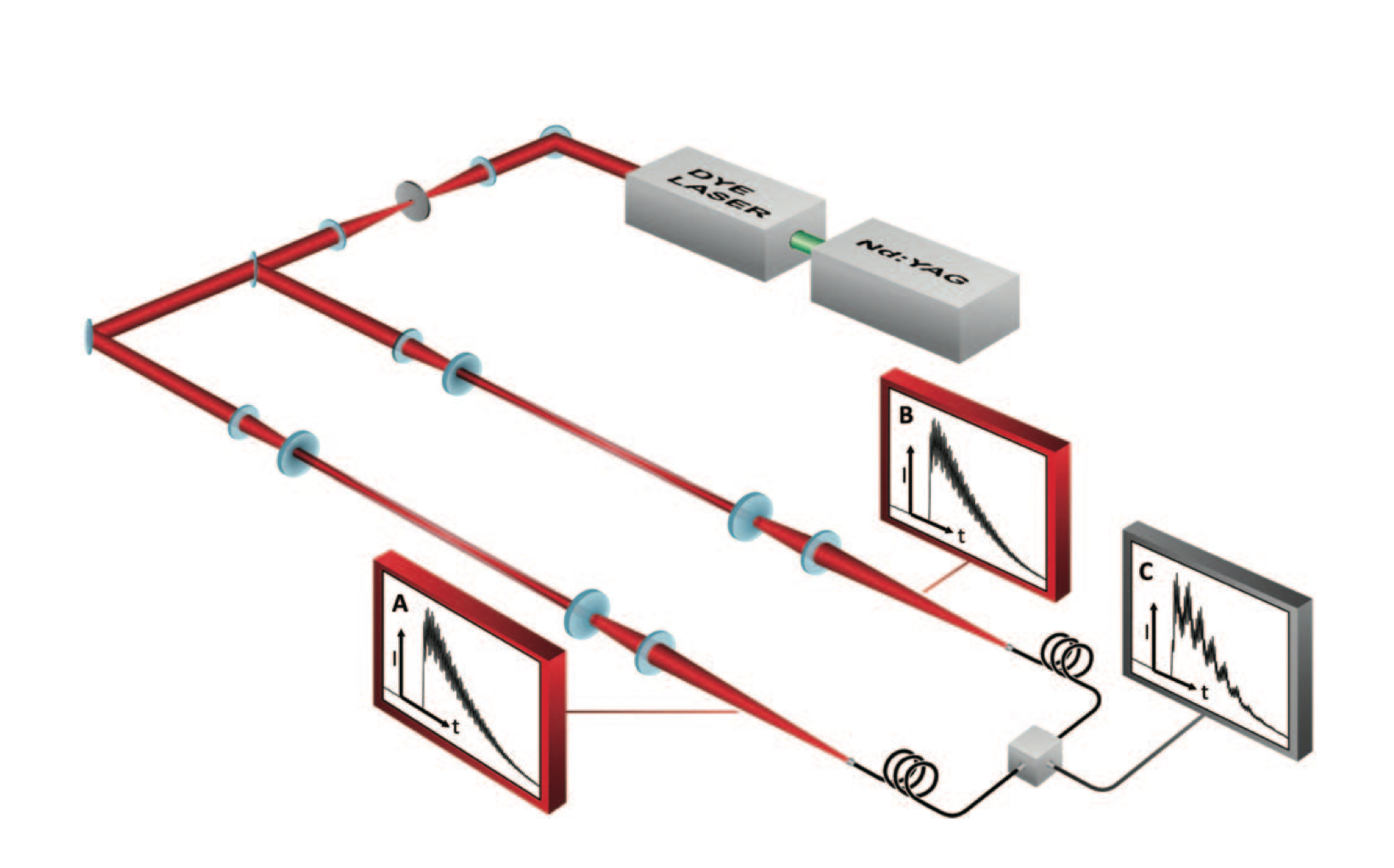
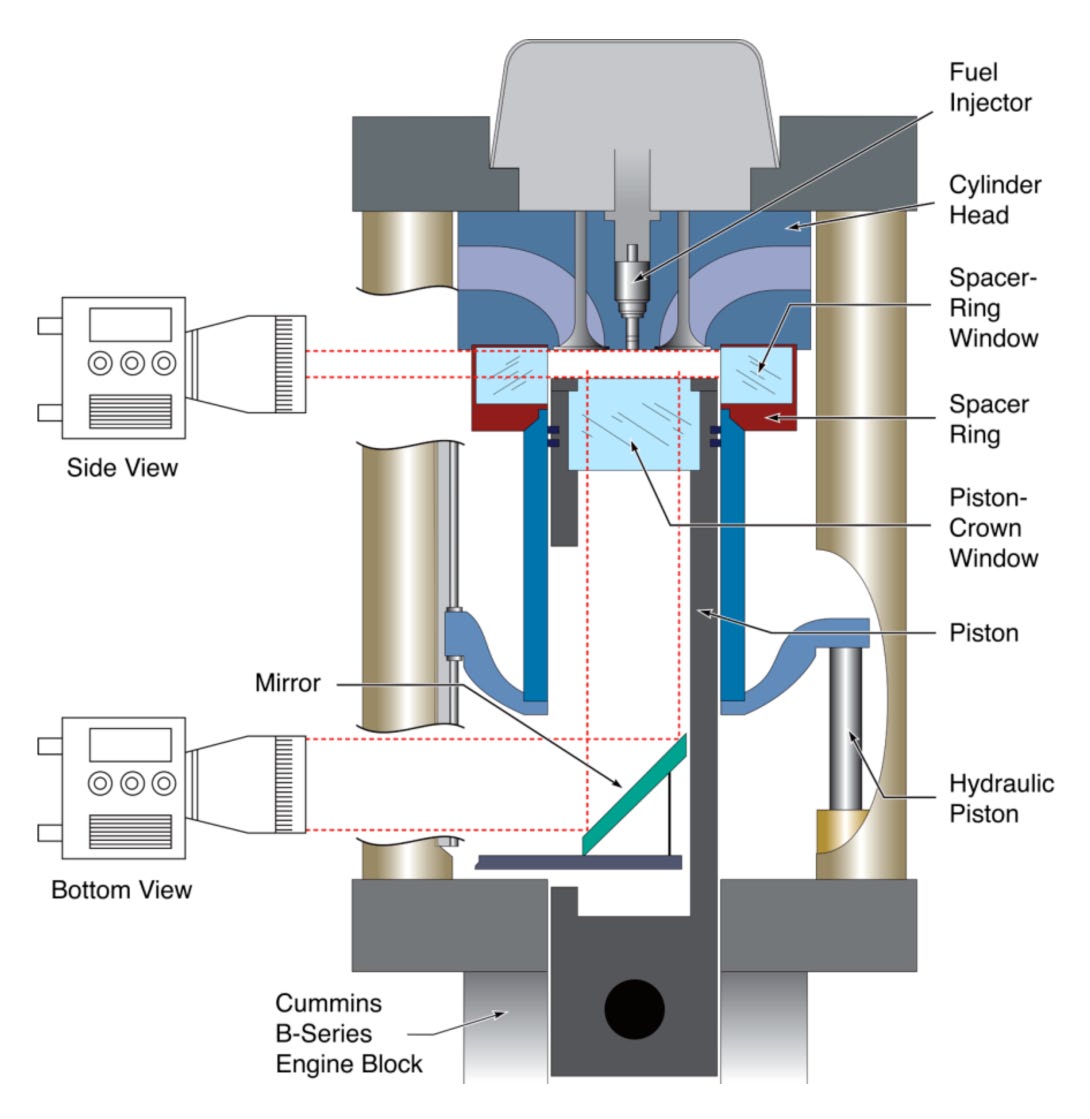
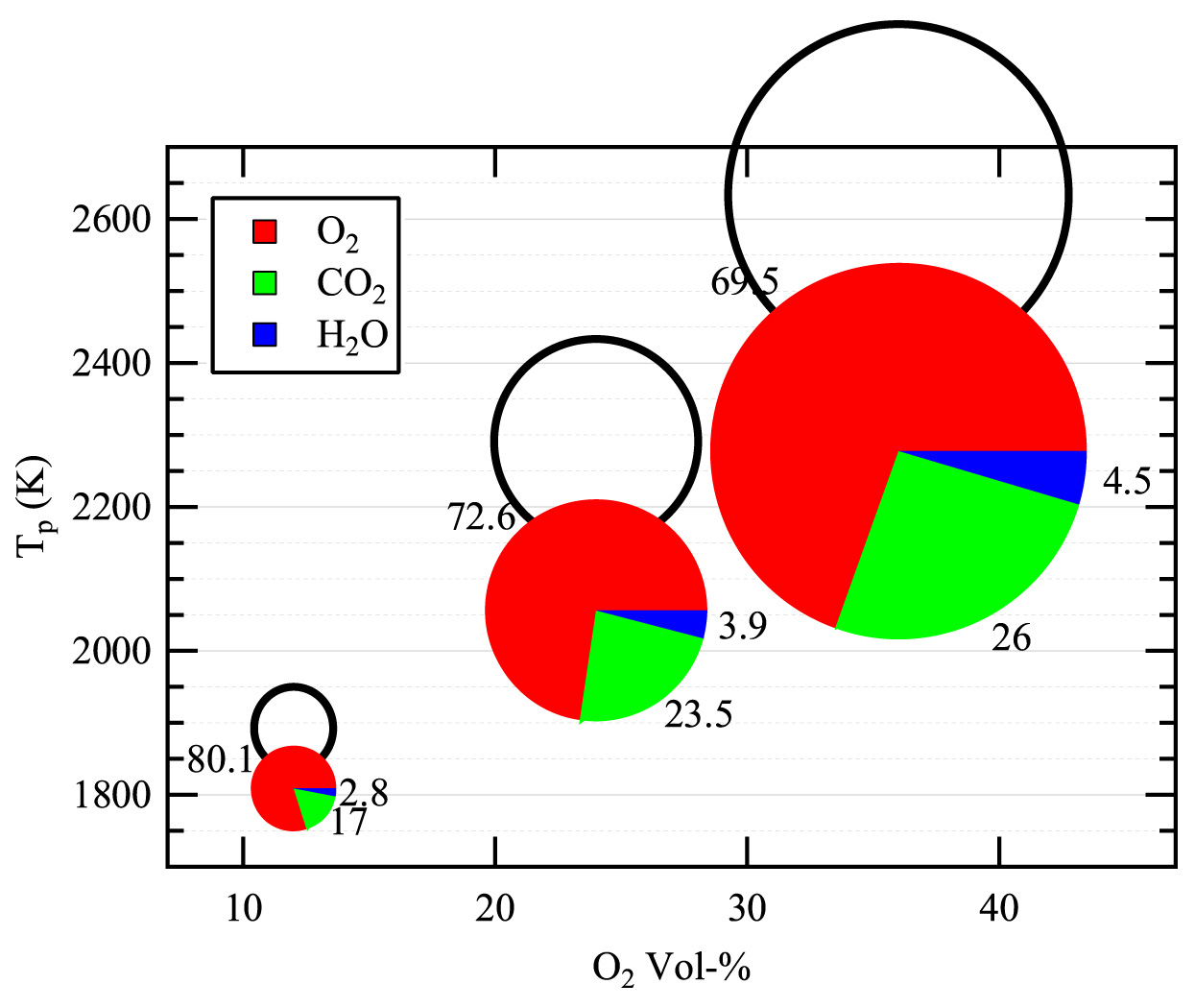
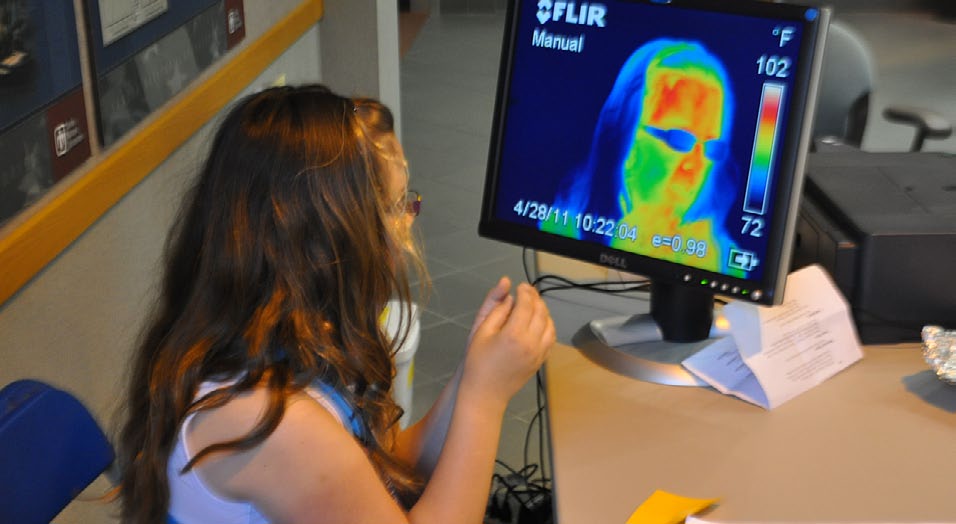
Post, November 22, 2013 • In developing the dual etalon frequency comb (DEFCOM) spectrometer, CRF researchers Haifeng Huang and David Chandler are refining a new concept for time-resolved Fourier-transform (FT) spectroscopy based on the interference between two transient frequency combs. By opening the door to many potential uses—including time-resolved, high-resolution, broad-band spectroscopy with a microsecond...